Wound healing assay
Wound healing is a complex process that requires strategic cell and tissue interaction. In most cases, this regeneration is accomplished through a well-regulated wound healing process. One of the many critically important functions of wound healing is individual and collective cellular migration. Cell migration occurs during many important physiological processes. However, cell migration is dysregulated in many pathological situations such as fibrosis. Myofibroblasts are implicated in the contraction of both wound tissue and the scar-like disease cords that define Dupuytren’s disease (DD). These cells not only regulate the remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM), but also produce growth factors that can promote scar formation, in the case of DD, or further tissue repair events during normal wound healing. Basal cell migratory potential of DD cells is much higher than that of normal palmar- derived fibroblasts. Myofibroblast/fibroblast migration and proliferation results in the development of the leading edges of progressive fibrotic lesions and the formation of fibrotic lesions generally are able to penetrate the surrounding tissues. Understanding this specific cellular function is important for translational medicine that can lead to improved wound healing outcomes.
To utilize the DD diseased myofibroblasts to screen the epigenetic probe set to determine whether any probes either enhance or inhibit cell migration. We are ultilzing the IncuCyte™ Scratch Wound assay to measure the movement of cells into a cell free zone. The Woundmaker™ creates a precise wound in each well and you can monitor wound closure as cells move across a collagen type I substrate.
We found the DD myofibroblasts particularly resistant to inhibitors of actin polymerization such as cytochalasin D and as such we used Latrunculin A instead. The most striking and novel result was observed with SGC-GAK-1 an inhibitor of cyclin G-associated kinase, which inhibited migration (91.4 % inhibition ± SD 4.7) to the same degree as our positive control Latrunculin A. The next most significant hit, with more modest levels of inhibition was BAY-850 (26% inhibition ± SD 5.6); an ATPase family AAA domain-containing protein 2 (ATAD2) inhibitor which has previously been shown to effect migration.
Analysing the donated probe set the 2 most significant results are the ERKi (56% inhibition ± SD 8) and the Cdc2-like kinases probe (T3-CLK, 72% inhibition ± SD 12) causing a significant inhibition of wound closure. The MAPK kinase pathways have previously been shown to regulate cellular migration but this possibility represents a novel function for the Cdc2-like kinases in wound healing.
- Surgically excised tissue from Dupuytren’s patients was treated with collagenase to derive single cell suspensions; cells were passaged (p2) and are termed myofibroblasts.
- Cells were seeded onto a Collagen type I coated (200ug/ml) 96 well plate at 7x103/well and probes were added at 1µM in triplicate, using DMSO as the vehicle control. Probes were incubated with the cells for 2 days.
- Media was removed and replaced with media containing Cell tracker green at a concentration of 2µM in Fluorobrite Media. Latrunculin A, an inhibitor of actin polymerisation is used as positive control, and is added to the respective well at this time at a concentration of 4uM and stained for 30 minutes.
- A wound is then made using the IncuCyte® woundmaker. All media is then replaced with media containing fresh probes at 1uM.
- Quantitative cell counting was then performed using the Celigo image cytometer at this time ( T=0)
- 24 hrs later whole-well images were acquired again using the Celigo Wound Healing application which reports the wound healing confluence and cell count for each well over time within the defined analysis area.
- Data is expressed as % compared to DMSO control (100%), DD1-4 Dupuytrens’s disease patients.
Epigenetic panel
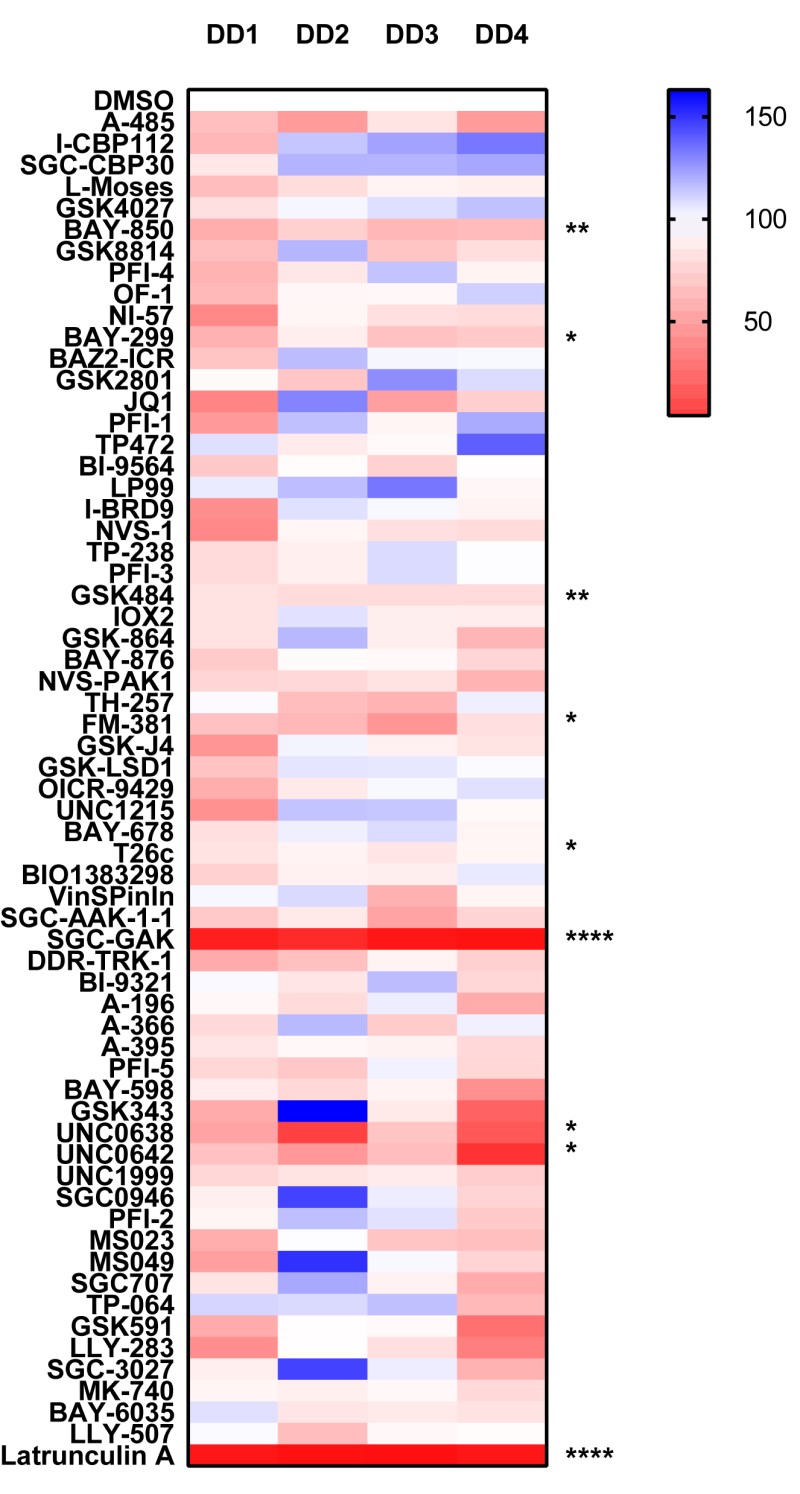
Donated panel
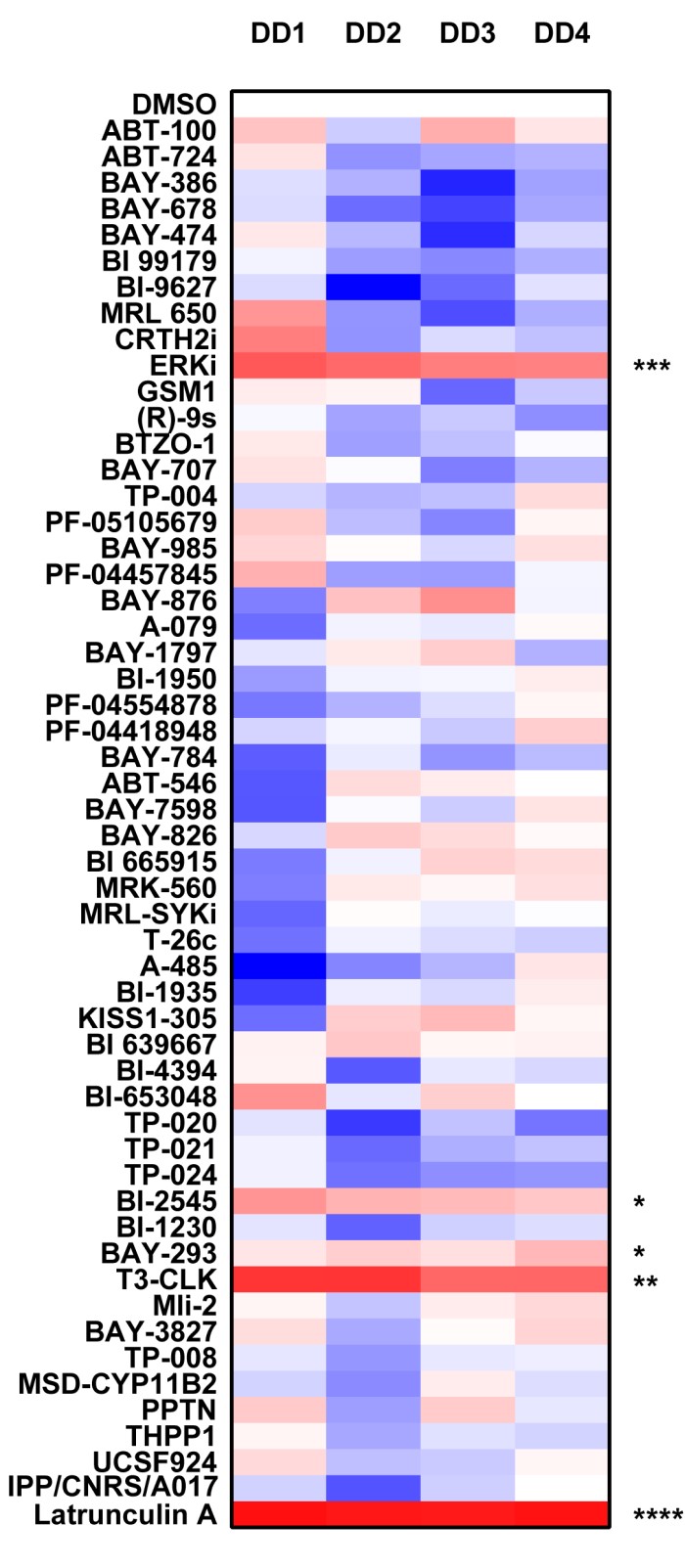
P value was determined by one sample t test to normalised control (DMSO) sample of 1.
P *<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001




